Ever wondered why some people seem to build wealth effortlessly while others struggle? The secret often lies in understanding and harnessing the power of compound interest. It’s not just for financial gurus; anyone can learn how to make their money work harder.
This article will demystify compound interest, explaining it in simple terms so you can start using it to your advantage today. You’ll learn how it works, how it’s calculated, and how to maximize its benefits. Let’s dive in and unlock the potential of compound interest explained simply.
What is Compound Interest?
Compound interest is essentially “interest on interest.” It’s the snowball effect in the financial world.
Instead of just earning interest on your initial investment (principal), you also earn interest on the accumulated interest from previous periods. This can lead to significant growth over time.
The Magic of Compounding: How It Works
Let’s say you invest $1,000 in an account that earns 5% annual interest. After the first year, you’ll have $1,050 ($1,000 + $50 interest).
In the second year, you’ll earn interest not just on the original $1,000, but on the entire $1,050. This means you’ll earn more than $50 in interest that year. The longer your money stays invested and compounds, the faster it grows.
Compound Interest vs. Simple Interest
It’s crucial to understand the difference between compound interest and simple interest. Simple interest is calculated only on the principal amount.
For example, with simple interest, that $1,000 investment at 5% would earn $50 each year, regardless of how long it’s invested. Compound interest, on the other hand, allows your earnings to grow exponentially over time.
The Compound Interest Formula: Demystified
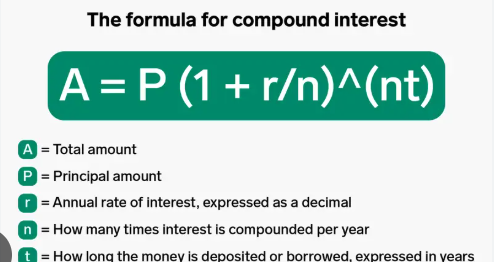
The formula for calculating compound interest might look intimidating, but it’s actually quite straightforward. Here it is:
A = P (1 + r/n)^(nt)
Where:
- A = the future value of the investment/loan, including interest
- P = the principal investment amount (the initial deposit or loan amount)
- r = the annual interest rate (as a decimal)
- n = the number of times that interest is compounded per year
- t = the number of years the money is invested or borrowed for
Let’s break it down with an example. If you invest $5,000 at an annual interest rate of 8% compounded quarterly for 10 years:
- P = $5,000
- r = 0.08 (8% as a decimal)
- n = 4 (compounded quarterly means 4 times a year)
- t = 10 years
A = $5,000 (1 + 0.08/4)^(4*10)
A = $5,000 (1 + 0.02)^(40)
A = $5,000 (1.02)^40
A ≈ $11,040.20
So, after 10 years, your investment would be worth approximately $11,040.20. This shows the power of compound interest explained simply in action.
Factors Affecting Compound Interest Growth
Several factors influence how quickly your money grows with compound interest:
- Principal Amount: The larger your initial investment, the more interest you’ll earn.
- Interest Rate: A higher interest rate leads to faster growth. Even small differences in interest rates can have a significant impact over the long term.
- Compounding Frequency: The more frequently interest is compounded (e.g., daily vs. annually), the faster your money grows.
- Time: The longer your money is invested, the more time it has to compound and grow. This is why starting early is crucial.
The Power of Time: Start Early!
Time is your greatest ally when it comes to compound interest. The earlier you start investing, the more time your money has to grow.
Even small amounts invested regularly over long periods can accumulate significant wealth. Don’t underestimate the power of starting small and staying consistent.
Where to Find Investments That Offer Compound Interest
Many investment options offer the benefits of compound interest:
- Savings Accounts: Traditional savings accounts and high-yield savings accounts typically offer interest that compounds daily or monthly.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): CDs offer a fixed interest rate for a specific period. The interest earned compounds over the term of the CD.
- Bonds: Bonds pay interest regularly, and this interest can be reinvested to earn even more interest.
- Dividend-Paying Stocks: Companies that pay dividends distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders. Reinvesting these dividends allows you to buy more shares and earn even more dividends over time.
- Retirement Accounts (401(k)s, IRAs): These accounts offer tax advantages and allow your investments to grow tax-deferred or tax-free, maximizing the benefits of compounding.
Maximizing Your Compound Interest Potential
Here are some strategies to maximize your compound interest potential:
- Start Saving Early: As we’ve emphasized, time is crucial. The earlier you start, the better.
- Increase Your Contributions: The more you save, the more your money can grow. Consider increasing your contributions over time as your income increases.
- Reinvest Your Earnings: Reinvest dividends, interest payments, and any other earnings to take full advantage of compounding.
- Choose Investments Wisely: Research different investment options and choose those that offer a balance of risk and return that aligns with your goals.
- Minimize Fees: High fees can eat into your returns and reduce the power of compounding. Look for low-cost investment options.
- Stay Consistent: Avoid withdrawing your money prematurely. The longer your money stays invested, the more it will grow.
Compound Interest and Debt: A Double-Edged Sword
While compound interest can be a powerful tool for wealth creation, it can also work against you when it comes to debt.
Credit card debt, loans, and other forms of debt often accrue compound interest. This means that if you don’t pay off your balance in full each month, the interest will be added to your balance, and you’ll start paying interest on the interest.
To avoid the negative effects of compound interest on debt:
- Pay Off High-Interest Debt First: Focus on paying off debts with the highest interest rates first.
- Make More Than the Minimum Payment: Making only the minimum payment on your debt will prolong the repayment period and result in you paying significantly more in interest.
- Avoid Taking on Unnecessary Debt: Be mindful of your spending and avoid taking on debt that you can’t afford to repay quickly.
Real-Life Examples of Compound Interest
Let’s look at some real-life examples to illustrate the power of compound interest:
- Retirement Savings: Imagine two people, Sarah and Tom. Sarah starts saving $5,000 per year at age 25, while Tom starts saving the same amount at age 35. Assuming an average annual return of 7%, Sarah will have significantly more money at retirement than Tom, even though they invested the same total amount. This is because Sarah’s money had 10 extra years to compound.
- Mortgage Payments: When you make mortgage payments, a portion of each payment goes towards principal and a portion goes towards interest. In the early years of your mortgage, a larger portion of your payment goes towards interest. As you pay down the principal, a larger portion of your payment goes towards principal, and you build equity faster.
- Credit Card Debt: If you carry a balance on your credit card and only make the minimum payment, it can take years to pay off the debt, and you’ll end up paying a significant amount of interest. This is because the interest is compounding on the unpaid balance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Compound Interest
- Waiting Too Long to Start: The biggest mistake is waiting too long to start saving and investing. Time is your greatest asset when it comes to compound interest.
- Withdrawing Money Prematurely: Withdrawing money before it has had a chance to compound can significantly reduce your long-term returns.
- Focusing on Short-Term Gains: Compound interest is a long-term strategy. Don’t get distracted by short-term market fluctuations.
- Ignoring Fees: High fees can eat into your returns and reduce the power of compounding.
- Not Reinvesting Earnings: Failing to reinvest dividends, interest payments, and other earnings means you’re missing out on the opportunity to maximize compounding.
Tools and Resources for Calculating Compound Interest
Numerous online calculators and resources can help you calculate compound interest and plan your investments:
- Online Compound Interest Calculators: Many websites offer free compound interest calculators that allow you to input your principal amount, interest rate, compounding frequency, and time period to see how your investment will grow.
- Financial Planning Software: Financial planning software can help you create a comprehensive financial plan that incorporates compound interest and other investment strategies.
- Financial Advisors: A financial advisor can provide personalized advice and guidance on how to maximize your compound interest potential.
Understanding the Impact of Inflation on Compound Interest
It’s important to consider the impact of inflation when evaluating the returns from compound interest. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time.
While your investment may grow due to compound interest, the real return (the return after accounting for inflation) may be lower. It’s essential to invest in assets that have the potential to outpace inflation to maintain your purchasing power.
The Psychology of Compound Interest
Understanding the psychology of compound interest can help you stay motivated and committed to your long-term financial goals.
It’s easy to get discouraged when you see slow progress in the early years. However, it’s important to remember that the power of compounding builds over time. Stay patient, consistent, and focused on your long-term goals, and you’ll be rewarded in the end.
Conclusion
Compound interest explained simply is a fundamental concept for anyone looking to build wealth. By understanding how it works, starting early, and making consistent contributions, you can harness the power of compounding to achieve your financial goals. Remember that time is your greatest ally, and even small amounts invested regularly can accumulate significant wealth over the long term.
Now that you understand the magic of compounding, what steps will you take to start maximizing its benefits? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!

