Ever feel like we’re just tossing things away, creating mountains of waste? What if there was a better way, a system that kept resources in use for as long as possible? That’s where circular economy principles explained clearly come into play.
This article will break down the core ideas behind this sustainable approach, showing you how it can benefit businesses, the environment, and even your own wallet. Get ready to dive into a world where waste becomes a resource and sustainability becomes the norm.
Understanding the Core of Circular Economy Principles
The circular economy is a model of production and consumption, which involves sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing and recycling existing materials and products as long as possible. It’s a stark contrast to the traditional linear economy, which follows a “take-make-dispose” pattern.
This approach aims to minimize waste and make the most of resources. By keeping materials in use, we reduce the need for new extraction and production, leading to a more sustainable future.
Key Differences: Linear vs. Circular
Think of it like this: the linear economy is like using a disposable coffee cup, while the circular economy is like using a reusable mug. One ends up in the trash almost immediately, the other keeps being used.
The linear model relies on continuous extraction of raw materials. The circular model focuses on keeping materials in circulation.
The Fundamental Principles of a Circular Economy
Several core principles guide the implementation of a circular economy. Understanding these principles is crucial for businesses and individuals alike.
1. Design Out Waste and Pollution
This is arguably the most important principle. It emphasizes designing products and systems that minimize waste from the outset.
This includes using durable materials, designing for disassembly, and avoiding harmful substances. Thinking about the entire lifecycle of a product during the design phase is key.
2. Keep Products and Materials in Use
The goal is to extend the lifespan of products and materials. This can be achieved through various strategies.
These strategies include repair, reuse, refurbishment, and remanufacturing. Keeping products in use reduces the need for new production.
3. Regenerate Natural Systems
A circular economy should contribute to the health of natural ecosystems. This means avoiding activities that deplete resources or damage the environment.
It also involves actively restoring natural systems through practices like reforestation and soil regeneration. The circular economy isn’t just about materials; it’s about the entire ecosystem.
Implementing Circular Economy Principles in Business
Businesses can play a huge role in driving the circular economy. By adopting circular practices, they can reduce costs, improve their brand image, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Circular Product Design
Designing products with circularity in mind is crucial. This involves considering factors like durability, repairability, and recyclability.
Companies can also use materials that are recycled or renewable. Modular design, which allows for easy replacement of parts, is another important aspect.
Closed-Loop Supply Chains
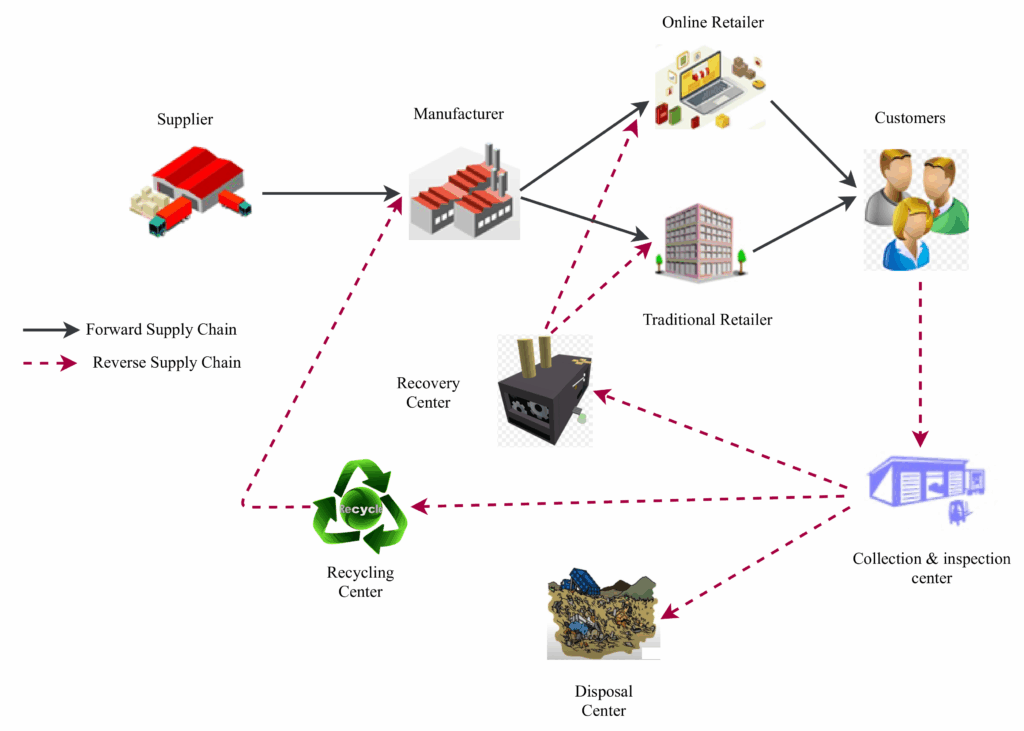
Closed-loop supply chains aim to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization. This involves recovering and reusing materials within the supply chain.
For example, a company might collect used products from customers and use them to manufacture new ones. This reduces the need for virgin materials and minimizes waste.
Product-as-a-Service (PaaS) Models
Instead of selling products outright, companies can offer them as a service. This incentivizes them to design products that are durable and long-lasting.
Examples include leasing clothing, renting tools, and subscribing to lighting services. The company retains ownership of the product and is responsible for its maintenance and repair.
Waste as a Resource
One company’s waste can be another company’s resource. Identifying opportunities to use waste materials as inputs for other processes is a key aspect of the circular economy.
For example, agricultural waste can be used to produce biofuels or compost. Industrial waste can be used to create new building materials.
The Benefits of Embracing Circularity
Adopting circular economy principles offers a wide range of benefits. These benefits extend beyond environmental protection and include economic and social advantages.
Environmental Benefits
The most obvious benefit is reduced waste and pollution. By keeping materials in use, we reduce the need for landfills and incinerators.
Circular economy also helps conserve natural resources and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. A more sustainable future is a key outcome.
Economic Benefits
Circular economy can create new business opportunities and jobs. Repair, refurbishment, and remanufacturing industries are growing rapidly.
It can also reduce costs by minimizing waste and optimizing resource utilization. Resource independence and reduced price volatility are other economic advantages.
Social Benefits
Circular economy can improve social equity by creating local jobs and promoting sustainable consumption patterns. It can also enhance community resilience by reducing dependence on global supply chains.
Increased consumer awareness and engagement are also positive social outcomes. People are becoming more conscious of their consumption habits.
Challenges to Implementing Circular Economy
Despite the many benefits, there are also challenges to implementing circular economy principles. Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration between businesses, governments, and individuals.
Lack of Awareness and Understanding
Many people are still unaware of the circular economy and its benefits. Raising awareness and educating the public are crucial steps.
Businesses also need to be educated about the opportunities and challenges of adopting circular practices. Knowledge is power.
Regulatory Barriers
Existing regulations may not be designed to support circular economy. Governments need to create policies that incentivize circular practices and remove barriers.
Extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, which hold producers responsible for the end-of-life management of their products, are one example of supportive policy.
Infrastructure and Technology
Implementing circular economy requires adequate infrastructure for collection, sorting, and processing of waste materials. Investing in new technologies is also essential.
Advanced recycling technologies, such as chemical recycling, can help process materials that are difficult to recycle using traditional methods.
Consumer Behavior
Changing consumer behavior is essential for the success of the circular economy. People need to be willing to repair, reuse, and recycle products.
Promoting sustainable consumption patterns and educating consumers about the benefits of circularity are crucial steps.
Circular Economy in Action: Real-World Examples
Many companies and organizations are already implementing circular economy principles successfully. These examples demonstrate the potential of circularity in various industries.
Patagonia: Repair and Reuse
Patagonia is a well-known example of a company committed to circularity. They offer repair services for their products and encourage customers to buy used clothing.
Their “Worn Wear” program allows customers to trade in used Patagonia clothing for store credit. This helps keep products in use for longer.
Interface: Closed-Loop Manufacturing
Interface, a carpet tile manufacturer, has implemented closed-loop manufacturing processes. They collect used carpet tiles from customers and recycle them into new products.
This reduces the need for virgin materials and minimizes waste. They are a pioneer in sustainable manufacturing.
Philips: Product-as-a-Service

Philips offers lighting as a service to businesses. Instead of selling light bulbs, they provide illumination and are responsible for maintenance and energy efficiency.
This incentivizes them to use durable and energy-efficient products. It’s a win-win for both the company and the environment.
The Role of Government in Promoting Circularity
Governments play a crucial role in creating a supportive environment for the circular economy. This includes setting policies, providing incentives, and investing in infrastructure.
Policy and Regulation
Governments can implement policies that promote circular practices, such as extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes and waste reduction targets. They can also create regulations that restrict the use of harmful substances.
Clear and consistent policies are essential for creating a level playing field for businesses. Regulations should be designed to incentivize innovation and promote sustainable practices.
Incentives and Funding
Governments can provide financial incentives to businesses that adopt circular practices. This can include tax breaks, grants, and subsidies.
Funding for research and development of circular technologies is also crucial. Investing in innovation is key to unlocking the full potential of the circular economy.
Public Procurement
Governments can use their purchasing power to promote circular economy. By prioritizing products and services that are designed for durability, repairability, and recyclability, they can create demand for circular products.
Public procurement can also be used to support local businesses that are committed to sustainability. Leading by example is a powerful way to drive change.
How Individuals Can Contribute to a Circular Economy
Individuals also have a role to play in the circular economy. By making conscious consumption choices and adopting sustainable habits, we can all contribute to a more circular future.
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
The classic “reduce, reuse, recycle” mantra is still relevant. Reducing consumption, reusing products, and recycling materials are all important steps.
Choosing durable products, repairing broken items, and buying used goods are all ways to reduce waste.
Support Circular Businesses
Support businesses that are committed to circularity. This can include buying products from companies that use recycled materials or offering repair services.
Vote with your wallet and choose businesses that align with your values. Consumer demand can drive significant change.
Educate Yourself and Others
Learn more about the circular economy and share your knowledge with others. The more people who understand the benefits of circularity, the more likely we are to achieve a sustainable future.
Talk to your friends, family, and colleagues about the circular economy. Spread the word and inspire others to take action.
Conclusion
The circular economy offers a compelling vision for a more sustainable future. By embracing its principles, we can reduce waste, conserve resources, and create new economic opportunities. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are immense.
From businesses redesigning products for circularity to governments implementing supportive policies and individuals making conscious consumption choices, everyone has a role to play. Let’s work together to build a circular economy that benefits both people and the planet. What steps will you take today to embrace circularity? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!
FAQ Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about circular economy principles.
What is the difference between recycling and circular economy?
Recycling is a component of the circular economy, but the circular economy is much broader. Recycling focuses on processing waste materials into new products. The circular economy encompasses the entire lifecycle of a product, from design to end-of-life management, with the goal of minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization.
How can businesses benefit from adopting circular economy principles?
Businesses can benefit from reduced costs, new revenue streams, improved brand image, and increased resource security. Circular practices can lead to greater efficiency, innovation, and resilience.
What are some simple ways individuals can contribute to the circular economy?
Individuals can reduce consumption, reuse products, recycle materials, support circular businesses, and educate themselves and others about the circular economy. Small changes in our daily habits can make a big difference.

